Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- vectorcalculus
- adaptivedensitycontrol
- rospackages
- turtlebot
- usbcamera
- Slam
- gaussiansplatting
- pointcloud
- vectorfields
- turtlebot3
- 3dmapping
- LIDAR
- rostopics
- covariancematrix
- raspberrypi
- realtimerendering
- roslaunch
- imageprocessing
- Ros
- electromagnetism
- alphablending
- catkinworkspace
- 3dgaussiansplatting
- NERF
- rosnoetic
- sensorfusion
- opencv
- differentiablerendering
- tilebasedrasterizer
- ComputerVision
Archives
- Today
- Total
Wiredwisdom
The Evolution of Programming Languages: A Historical Overview 본문
Computer Science/Basic
The Evolution of Programming Languages: A Historical Overview
Duke_Ryan 2024. 11. 29. 21:22

section .data
msg db 'Hello, World!', 0Ah ; 출력할 메시지와 줄바꿈(0Ah)
len equ $ - msg ; 메시지 길이 계산
section .text
global _start ; 프로그램 시작점 선언
_start:
; write 시스템 콜 사용
mov eax, 4 ; 시스템 콜 번호 (sys_write)
mov ebx, 1 ; 파일 디스크립터 (stdout)
mov ecx, msg ; 메시지 주소
mov edx, len ; 메시지 길이
int 80h ; 커널 호출
; exit 시스템 콜 사용
mov eax, 1 ; 시스템 콜 번호 (sys_exit)
mov ebx, 0 ; 종료 코드 0 (정상 종료)
int 80h ; 커널 호출
section .bss
buffer resb 64 ; 64바이트 버퍼 예약; 데이터 섹션의 바이너리 표현
; msg db 'Hello, World!', 0Ah
48 65 6C 6C 6F 2C 20 57 6F 72 6C 64 21 0A
; _start 레이블부터 시작되는 코드 섹션의 바이너리 표현
; write 시스템 콜
B8 04 00 00 00 ; mov eax, 4
BB 01 00 00 00 ; mov ebx, 1
B9 XX XX XX XX ; mov ecx, msg (실제 주소값으로 대체됨)
BA 0E 00 00 00 ; mov edx, 14 (메시지 길이)
CD 80 ; int 80h
; exit 시스템 콜
B8 01 00 00 00 ; mov eax, 1
BB 00 00 00 00 ; mov ebx, 0
CD 80 ; int 80h
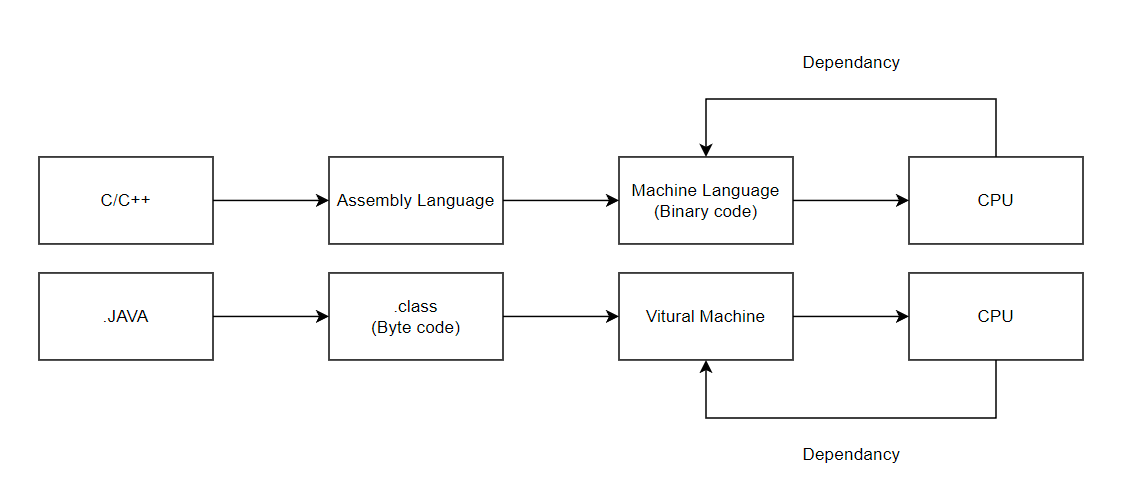
1940s - The Beginning
- Machine Code & Assembly
- First generation: Pure binary machine code
- Assembly language introduced as the first human-readable abstraction
- Key development: ENIAC (1946) programmed through physical rewiring
1950s - The Foundation
- High-level Languages Emerge
- FORTRAN (1957) - First widely used high-level language
- LISP (1958) - First functional programming language
- COBOL (1959) - Business-oriented language
1960s - Structured Programming
- Key Paradigm Shifts
- ALGOL 60 - Introduced block structure and scope
- BASIC (1964) - Simplified programming for beginners
- Simula (1967) - First object-oriented programming language
1970s - The Unix Era
- Systems and Modern Languages
- C (1972) - Unix development and systems programming
- Pascal (1970) - Structured programming emphasis
- Smalltalk (1972) - Pure object-oriented programming
- SQL (1974) - Specialized database language
1980s - Object-Oriented Revolution
- OOP Goes Mainstream
- C++ (1983) - OOP features added to C
- Ada (1983) - Department of Defense standard
- Perl (1987) - Text processing and system administration
1990s - The Internet Age
- Web and Enterprise
- Python (1991) - Emphasis on readability
- Java (1995) - "Write once, run anywhere"
- JavaScript (1995) - Client-side web programming
- PHP (1995) - Server-side web development
- Ruby (1995) - Developer happiness focus
2000s - Modern Development
- Framework and Productivity Focus
- C# (2000) - Microsoft's Java competitor
- Scala (2004) - Functional meets object-oriented
- Ruby on Rails (2004) - Web framework revolution
2010s - New Generation
- Cloud and Concurrency
- Go (2009) - Modern systems programming
- Rust (2010) - Memory safety without garbage collection
- Swift (2014) - Modern Apple development
- Kotlin (2011) - Modern JVM language
2020s - AI and Future Directions
- Intelligence and Safety
- Focus on AI/ML specialized languages and tools
- Emphasis on type safety and concurrent programming
- Rise of domain-specific languages (DSLs)
Key Trends Throughout History
- Increasing Abstraction
- From machine code to visual programming
- Higher-level concepts and automation
- Paradigm Evolution
- Procedural → Structured → Object-Oriented → Functional
- Hybrid approaches becoming common
- Safety and Reliability
- Type systems becoming more sophisticated
- Built-in testing and verification tools
- Performance vs. Productivity
- Constant balance between execution speed and development speed
- Domain-specific optimizations
- Platform Independence
- Movement from machine-specific to portable code
- Rise of virtual machines and runtime environments
'Computer Science > Basic' 카테고리의 다른 글
| C compile process (0) | 2025.07.27 |
|---|---|
| UBUNTU Setup 우분투 설치 종류 (1) | 2024.01.09 |


